The menopause support market holds big growth potential
Outlook
1.2 billion women by 2030
With the aging of the population, it is estimated that there will be 1.2 billion of menopausal women by the year 2030.
50 symptoms associated
There are around 50 symptoms associated with menopause.
Awareness of menopausal symptoms
Awareness of menopausal symptoms and long-term health implications continues to grow.
It represents 1/3 of a woman's life
Women spend one-third of their lives in menopause.
440% growth in interest
Probiotics for menopause have gained popularity since mid-2022, with a surge in online engagement, especially in Canada (+440%), the UK (+200%), Brazil (+50%), South Korea (+42%), and Italy (+33%).
931 M dollars in sales
The category of food supplements for menopausal symptoms reached 931 million dollars in sales in 2022 in the US.
Let's connect
KABP® Menopause is a probiotic formulation to modulate hormonal levels during menopause
Contact us to learn moreMenopausal symptoms can greatly disrupt a woman’s life
The end of an era
Menopause is a natural biological process experienced by all aging women, that marks the end of their reproductive years.
Menopausal transition starts when the ovaries slow down their function, causing changes in several hormone levels including follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), estrogen, and progesterone. It can last up to 10 to 15 years1.

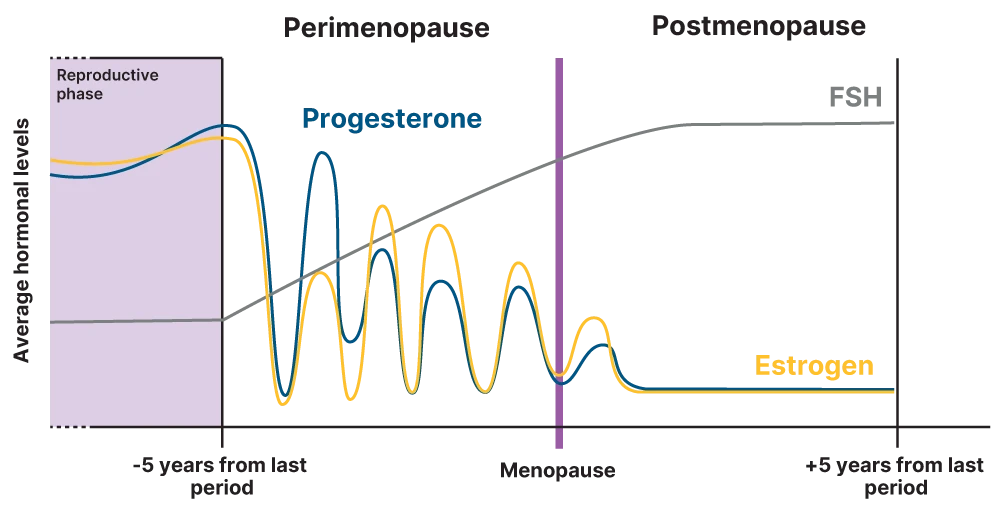
Approximately 80% of women will experience noticeable symptoms during menopause that can impact their quality of life3.
Symptoms
The fall in estrogen at menopause results in many changes throughout women’s bodies, including physical and psychological symptoms that vary in severity, duration, and manifestation1.
Brain function
- Vasomotor symptoms (hot flushes, sweating)
- Sleep disturbances
- Mood changes
- Decline in memory and concentration
- 2
Gut microbiome
- Loss of diversity
- 3
Adipose tissue and lipid metabolism
- Weight gain
- Redistribution of body fat (increased visceral fat)
- 4
Skin and mucosal barriers
- Loss of elasticity, thickness and hydration
- Increment of wrinkles
- Fragility of gut and urinary mucosa
- 5
Urogenital system
- Vaginal dryness
- Itching and burning
- 6
Sexual function
- Decreased sexual desire
- Painful intercourse
- 7
Musculoskeletal system
- Joint discomfort
- Reduction of lean muscle mass
- Decline of bone health
Accepted set by Probiotics Division
** both groups experienced symptom relief
As a natural, biological process, menopause should be addressed with solutions
Self care

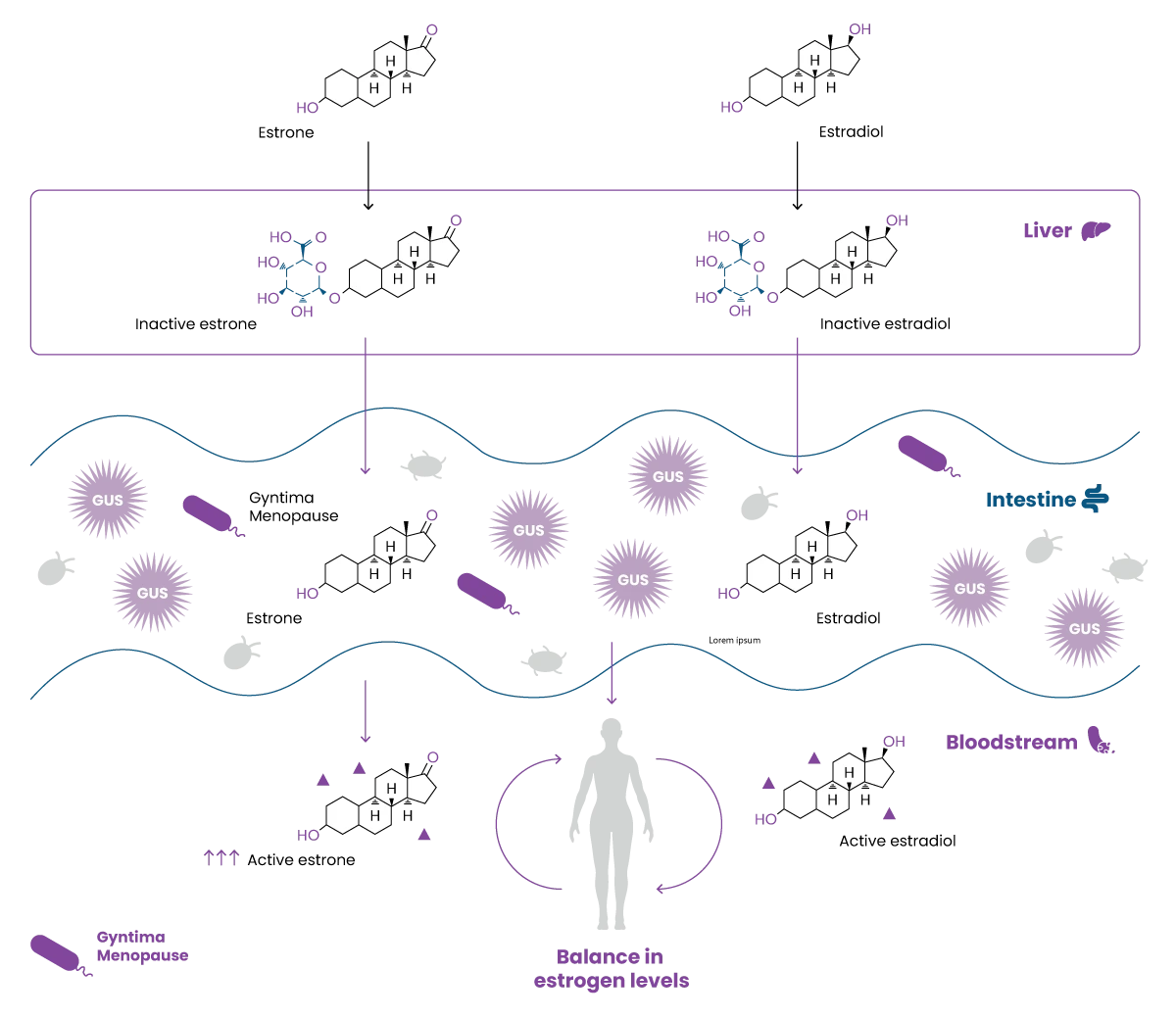
Gut microbiota modulates estrogen levels in the gut
Before being eliminated out of the body, estrogens are transformed into inactive forms by the liver. In the gut, estrogens can be rescued by specific commensal bacteria that convert estrogens into active molecules.
Estrogen reactivation occurs due to gut microbial b-glucuronidase (GUS) activity. In the gut, GUS activity facilitates the reabsorption of active estrogens in the bloodstream, contributing to the modulation of estrogen pool in the body.
During menopausal transition, the gut microbiota reduces its diversity and there is a loss of microbial GUS activity, which negatively impacts estrogen levels6.
KABP® Menopause slows down estrogen decline through GUS activity
A better way
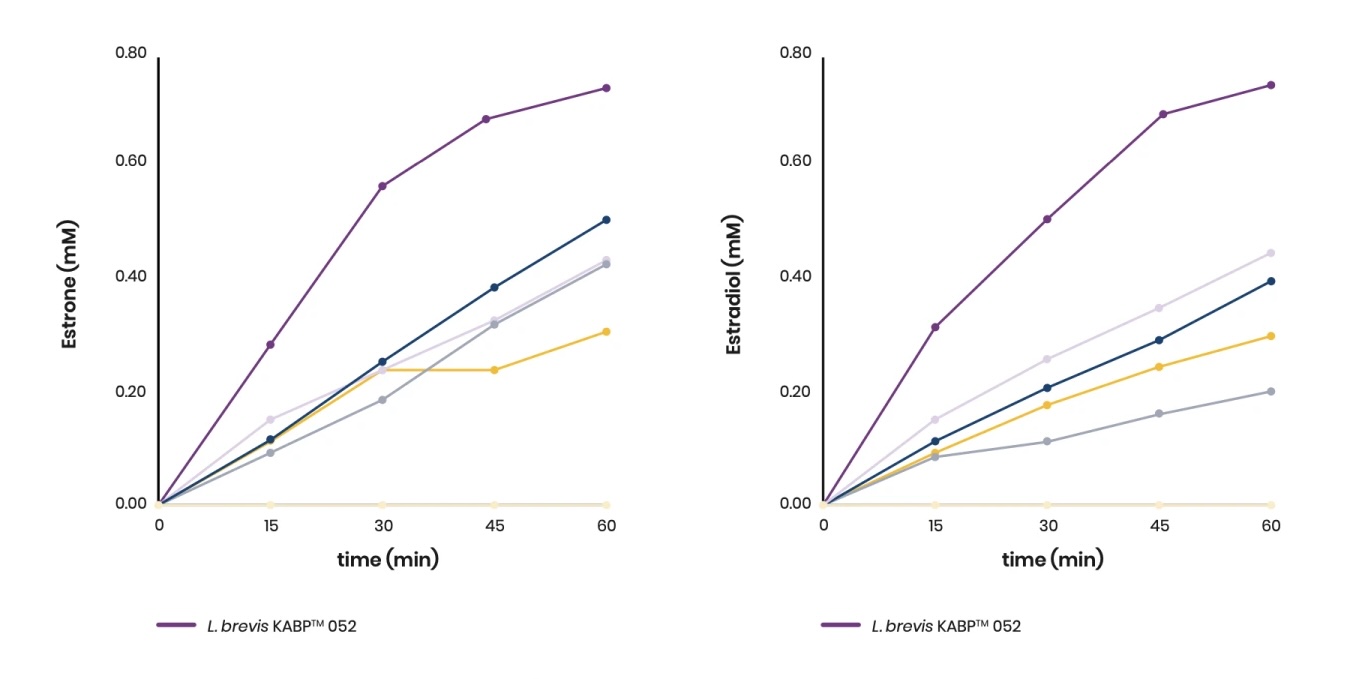
After an in vitro screening of over 80 bacterial strains from 16 different probiotic species, L. brevis KABP® 052 stood out with the strongest GUS activity.
Estrone and estradiol are two forms of estrogen that play crucial roles in the female body.
KABP® Menopause is a probiotic formulation demonstrated to modulate hormonal levels in a clinical trial.














Estrogen plays a crucial role in women’s health
Bring balance to your body
Essential for the functioning of the reproductive system.
Contributes to skin hydration, elasticity and thickness, and hair growth and quality.
Supports cognitive function, memory, and mood regulation.
Supports the cardiovascular system by promoting healthy blood vessels.
Helps maintain bone density and strength.
The strain L. brevis KABP® 052 demonstrated a significant ability to reactivate estrogens
The ability of KABP® Menopause strains to reactivate estrogens was also studied. After 1 hour of incubation, L. brevis KABP® 052 produced significantly higher levels of deconjugated (active) estrogens than the other strains evaluated.
** Both groups experienced symptom relief
A clinical study found that KABP® Menopause reduces the decline in estrogen levels in menopausal women11
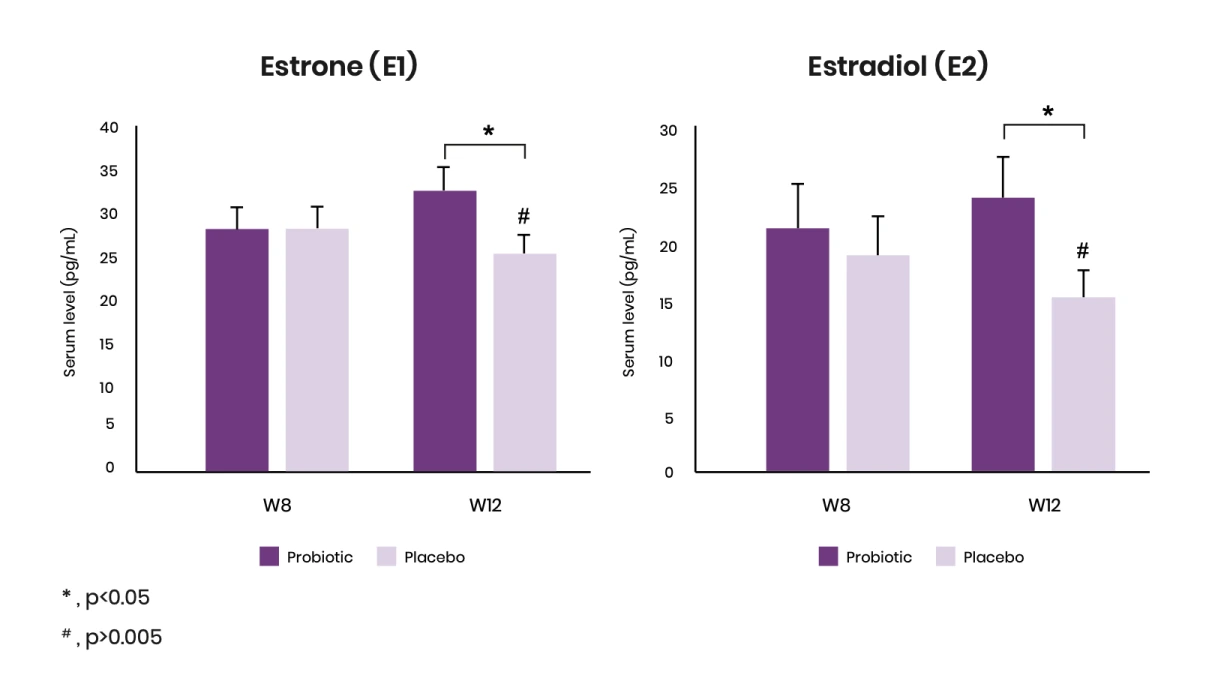
Results
- Estrone and estradiol levels in placebo group were reduced at week 12 compared to baseline (#) while they were maintained in probiotic group.
- The probiotic reduces the decline of E1 and E2 levels compared to placebo after 12 weeks of treatment.
There were no significant differences between the groups with respect to a reduction in menopause symptoms
KABP® Menopause: Proprietary, tailored probiotic formulation for a balanced menopause journey
Start a new chapter
KABP® Menopause is an ideal choice for...
Perimenopausal women who want to proactively manage their health and well-being throughout the menopause journey, seeking safe and effective products that may help enable them to maintain an active and healthy lifestyle.

Recommended use
- One capsule daily
References
- Davis, S. R. et al. Menopause. Nat Rev Dis Primers 1, (2015)
- Schoenaker, D. A. J. M., Jackson, C. A., Rowlands, J. V. & Mishra, G. D. Socioeconomic position, lifestyle factors and age at natural menopause: a systematic review and meta-analyses of studies across six continents. Int J Epidemiol 43, 1542–1562 (2014)
- Menopause at work | TUC. https://www.tuc.org.uk/menopause-work.
- Manson, J. A. E. et al. Menopausal Hormone Therapy and Health Outcomes During the Intervention and Extended Poststopping Phases of the Women’s Health Initiative Randomized Trials. JAMA 310, 1353–1368 (2013).
- Pinkerton, J. A. V. et al. The 2017 hormone therapy position statement of the North American Menopause Society. Menopause 24, 728–753 (2017).
- Ervin, S. M. et al. Gut microbial β-glucuronidases reactivate estrogens as components of the estrobolome that reactivate estrogens. Journal of Biological Chemistry 294, 18586–18599 (2019).
- Chen, P., Li, B. & Ou-Yang, L. Role of estrogen receptors in health and disease. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 13, (2022).
- Odai, T. et al. Severity of hot flushes is inversely associated with dietary intake of vitamin B6 and oily fish. Climacteric 22, 617–621 (2019).
- Management of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women: the 2021 position statement of The North American Menopause Society. Menopause 28, 973–997 (2021).
- Lucas, M., Asselin, G., Merette, C., Poulin, M. J., & Dodin, S. (2009). Ethyl-eicosapentaenoic acid for the treatment of psychological distress and depressive symptoms in middle-aged women: a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 89(2), 641-651.
- Honda et al. Supplementation with a probiotic blend increases serum estrogen levels in the peri/postmenopausal women. J Med Food (Accepted).
- Bani S, Hasanpour S, Farzad Rik L, Hasankhani H, Sharami SH. The effect of folic Acid on menopausal hot flashes: a randomized clinical trial. J Caring Sci. 2013 Jun 1;2(2):131-40. doi: 10.5681/jcs.2013.016. PMID: 25276719; PMCID: PMC4161099.


